Vendor Evaluation
Explanations
Vendor Evaluation Explanations
Rotek Incorporated will assess and evaluate the performance offered by its material Vendors semi-annually. The following criteria will be evaluated:
• Delivery Performance
• Quality Performance
• Price Performance
Each of these specific criteria will be awarded between 1 and 100 points. Overall scoring will be a combination of these three criteria, however, each category must be viewed separately. All Vendors are expected to strive for the maximum number of points. The final classification of their evaluation is derived from the following point scale:
Points Assessment / Measures Required
100 – 81 Outstanding Performance
The Vendor is not required to respond to the evaluation, and is considered preferentially by the Buyer when placing orders.
80 – 61 Good Performance
The Vendor’s performance is considered acceptable, but continuous improvements are encouraged.
60 – 41 Average Performance
The Vendor is required to provide a written response to the evaluation, and must identify their plan to improve performance. A new date for an interim evaluation may be warranted to verify implementation of corrective actions. Orders placed with the Vendor are exercised with caution and possibly to a restricted or limited extent. The Vendor is notified of their responsibility to assume any added cost due to the need for increased examination or inspection deemed appropriate to verify compliance on future deliveries of product. The Vendor is labelled as “Under Performance Observation”.
40 – 01 Re-qualification Required
The Vendor is required to provide a written response to the evaluation, must identify their plan to improve performance, and accept a mandatory, agreed-upon timeline for the improvement of performance. A personal meeting between Buyer and the Vendor may be warranted. The Vendor is notified of their responsibility to assume any additional costs due to increased examination or inspection of their product as a result of the evaluation. The Vendor is placed on a more frequent audit schedule and any poor performance on subsequent evaluations or audits will result in the complete disqualification of the Vendor.
Specific evaluation of Vendor Performance criteria are based on the following:
Criteria 1: Delivery Performance
Assessed by the Materials Management Department
Overall delivery performance is divided into two separate performance groups; On-time Delivery Performance and Quantity Reliability. The overall scoring of delivery performance is obtained by recording all delivery activity for the Vendor, and applying a weighting factor between On-time Delivery Performance and Quantity Reliability.
The weighting factor is 60% for On-time Delivery Performance and 40% for Quantity Reliability.
Only those purchase orders for whose delivery dates fall within the specified period and are actually received will be counted. Receipt is defined as physical arrival of the goods. If required, a detailed account of specific, individual performances my be provided to the Vendor.
On-Time Delivery Performance
Any deviation from the delivery due date (contractual delivery obligation on the Rotek Purchase Order) and the actual date received is measured in plus or minus days. In the example below, a “+” indicates a delivery that is made later than the delivery due date, and a “-“indicates a delivery is made earlier than the delivery due date. Vendors are required to deliver in accordance with the specific delivery due date, and not to weekly objectives, as this may cause the delivery performance to deviate unnecessarily.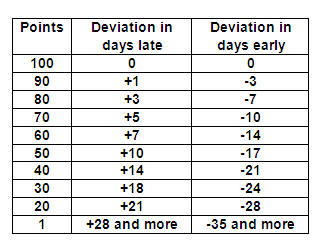
Example: A Purchase Order is placed and acknowledged for delivery of a material on November 11, 2009. Actual delivery and receipt occurs on November 18, 2009. The deviation to required delivery is 5 days. In observing the values on the table above, the late delivery of 5 days corresponds with a point value of 70 in the performance table. If this were the only delivery made by the Vendor, their score would be a 70.
Quantity Reliability
Quantity Reliability is a measure of the Vendor’s ability to provide the right quantity of a material (in accordance with the Purchase Order) when the material is shipped and received at Rotek. In the example below, a “+” indicates a delivery quantity that is made in excess of the required quantity on the Purchase Order, and a “-“indicates a delivery quantity is made that is less than the required quantity on the Purchase Order. 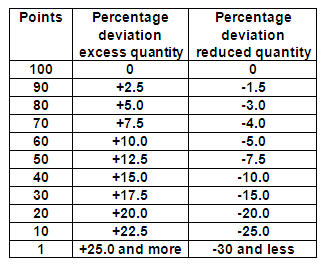
Example: A Purchase Order is placed and acknowledged for delivery of 100 units of a material. When the delivery is made, only 95 units arrive. The deviation is 5% of the line item total, so the Vendor receives a score of 60 points for the short delivery.
Criteria 2: Quality Performance
Assessed by the Quality Department
Overall Quality performance is divided into three separate performance groups; Total Quantity Rejected v. Total Quantity Received, Required Documentation, and Quality Management System. The overall scoring of Quality performance is obtained by recording all Quality activity for the Vendor, and applying a weighting factor between Quantity Received v. Rejected, Required Documentation, and Quality Management System.
The weighting factor is 50% for Rejection v. Receipts, 30% for Required Documentation, and 20% for Quality Management System.
Quantity Rejected v. Total Quantity Received
A measure of the percentage of materials received that are discrepant.
Required Documentation
A measure of how well a Vendor did in providing all necessary documentation such as drawings, inspection reports, etc. in the performance of the required delivery.
Quality Management System
A measure of a Vendor’s overall Quality Management System.
Criteria 3: Price Performance
Assessed by the Materials Management Department
Overall Price performance is divided into two separate performance groups; Price Level and Price Trend. The overall scoring of price performance is obtained by recording all price activity for the Vendor, and applying a weighting factor between Price Levels and Price Trends.
The weighting factor is 60% for Price Level and 40% for Price Trend.
Price Level
The price offered by a Vendor for a material during the report period is compared in relation to the market price. The market rate is a comparison of all valid prices from all Vendors of such material during the report period.
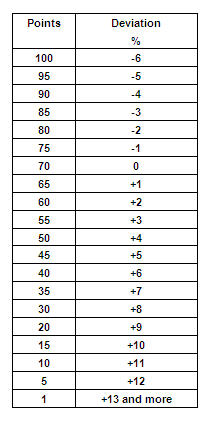
In the example below, a “+” indicates that a price offered by a Vendor is greater than the market rate, while a “-“ indicates that a price offered by a Vendor is lower than the market rate.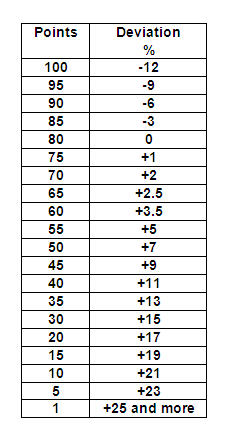
Example: In comparing the price offered by Vendor “A” of $100 per unit, Vendor “B” offers the same material for $84 per unit and Vendor “C” offers it for $110 per unit. The market rate is determined to be an average of the total market prices divided by the total number of suppliers ($100 + $84 + $110) / 3 = $98 per unit. Vendor “A” therefore compares with a deviation of +2% and is awarded a score of 70.
Price Trend
The price trend offered by a Vendor is compared to the rate of the trend in the market. In the example below, a “+” indicates that a price offered by a Vendor is greater than the market trend rate, while a “-“ indicates that a price offered by a Vendor is lower than the market trend rate.
Example: The average market price (all Vendors) fell by 5% from the original $100 per unit to the current price of $95 per unit. Vendor “A” has raised their price from $120 per unit to $122 per unit, or a 1.5% increase.
Example calculation:
1. Vendor “A” former pricing was $120 per unit, and should have been expected to follow the market trend of -5%, resulting in a price of $114 per unit.
2. The actual price development of Vendor “A” was from $120 per unit to $122 per unit, or a 1.5% increase.
3. The analysis of Vendor “A” with regard to the market rate is that their actual price of $122 per unit should be compared to the average rate of $114 per unit, resulting in a +7% increase.
4. A deviation of +7% results in a score of 35 as shown below.